Often, when an allergic reaction causes angioedema, it also produces hives. These itchy welts may appear on any part of your body, but they are most common on the hands and feet, the back of the throat, lips, mouth or tongue, and genitals.
Sometimes a person develops angioedema without hives—this is called idiopathic angioedema. It usually recurs and is not caused by any specific trigger.
1. Swelling of the lips
Swelling of the lips is a common angioedema sign. It can be caused by a variety of things, including allergic reactions, infections and cysts called mucoceles. In some cases, swelling of the lips can be severe or life-threatening and needs to be treated with epinephrine.
Other symptoms of angioedema include itching and a burning sensation on the swollen area. Sometimes, a person may experience mild diarrhea as well.
A doctor will do a physical exam and ask questions about the swelling. They will want to know what foods, medications and supplements you are taking. They will also do blood tests or allergy testing to determine the cause of your symptoms. They will probably recommend that you carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) with you at all times to treat a life-threatening allergic reaction.
2. Swelling of the tongue
If the tongue swells to a point where it is uncomfortable and makes eating difficult, talk with your doctor right away. You might have a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening (anaphylaxis) and requires emergency treatment. Your doctor may order skin prick tests and blood tests to check for allergies, a problem with your C1 inhibitor protein, or other conditions that cause angioedema.
In some cases, the swelling can be so deep that it causes difficulty breathing or even a swollen throat, which is a medical emergency that needs to be treated with epinephrine. The symptoms usually appear quickly and may include welts, or raised bumps that are itchy and red. They can be anywhere on the body, including the eyes and lips, arms and hands, and legs or genitalia.
3. Swelling of the throat
An allergic reaction to food, medication, insect stings or latex can trigger swelling of the throat. The swelling may be accompanied by hives and a drop in blood pressure. If the allergy is severe, it can be life-threatening. This is called anaphylaxis and requires immediate medical care. Common food allergens include shellfish, fish, eggs, milk, peanuts and tree nuts. Common medications that cause allergic reactions to the throat include penicillins, sulfa drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Allergies to venom from stinging insects and to latex (used in gloves and balloons) are also common.
Patchy red or pink areas of skin, sometimes described as welts, occur along with the swelling. Often these areas are not itchy. They can be on the hands and feet, the lips or tongue, the back of the throat or genitals.
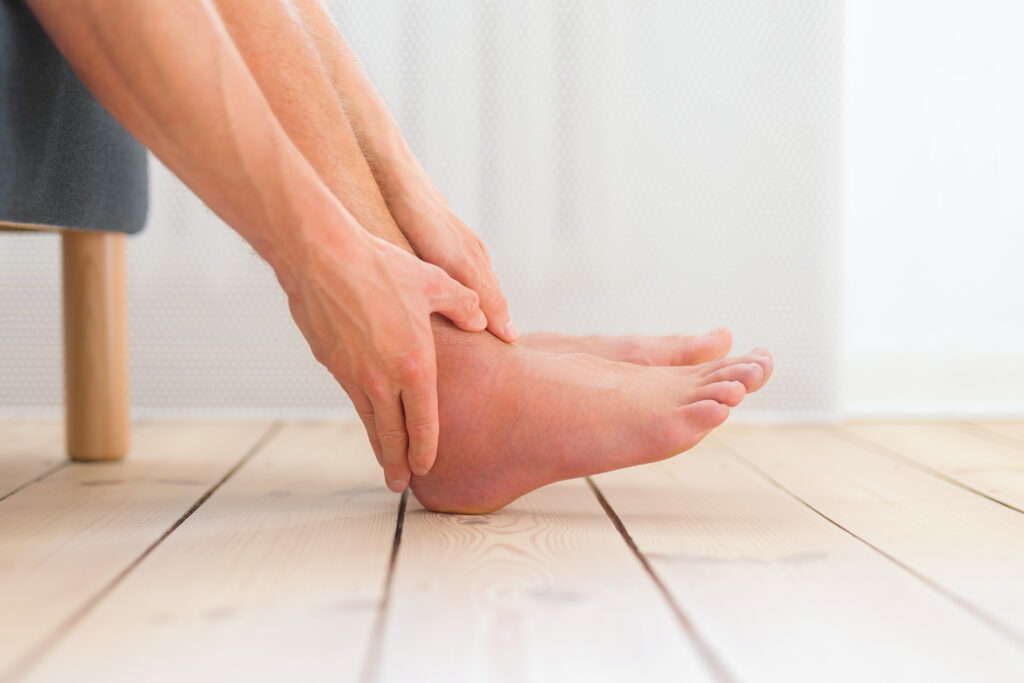
4. Swelling of the hands or feet
Occasionally, angioedema may occur without any identifiable trigger. This type of angioedema is called idiopathic or hereditary angioedema, and symptoms develop more slowly over the course of a couple of days.
Swelling of the hands or feet can be caused by a number of things, including:
A sedentary lifestyle: If you're sitting or lying down for extended periods, this can cause fluid to build up in different parts of your body. Excess sodium intake: Foods high in salt (sodium) can cause you to retain water.
You can treat mild angioedema with antihistamines, which reduce the release of histamine, which is one of the main causes of swelling. You might also need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector so that you can respond quickly if your throat or tongue starts to swell.
5. Swelling of the face
The swelling of the face (or lips, mouth or throat) can be a sign of a severe allergic reaction that requires emergency treatment in hospital. This is called anaphylaxis.
This can be caused by eating certain foods - shellfish, fish, eggs or dairy products - or by taking some medications, particularly antibiotics like penicillin, sulfa drugs or NSAIDs (aspirin) and ACE inhibitors used to treat high blood pressure or heart problems. Venom from bees, wasps and snakebites or natural rubber latex (found in balloons, condoms or gloves) can also trigger this type of allergy.
For this reason, people who have a history of this type of allergy should carry an epinephrine auto-injector (such as EpiPen) at all times. They should also avoid any food or medication that might trigger an allergy and see a specialist to confirm the cause of their problem.





