Introduction:
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder that affects red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. In sickle cell anemia, the red blood cells become misshapen and resemble a crescent or sickle, hence the name.
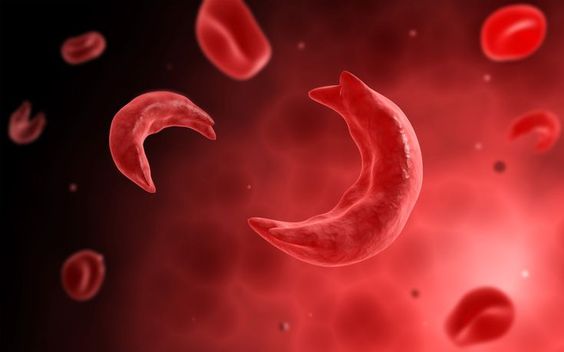
These abnormally shaped cells can block blood vessels, leading to a variety of complications. Sickle cell anemia is a serious condition, but with proper management, individuals can live full and productive lives. This article will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options associated with sickle cell anemia.
Understanding Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the gene that makes hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the body. The mutated gene causes the body to produce abnormal hemoglobin called hemoglobin S.
When red blood cells containing hemoglobin S release oxygen, they become stiff and sticky, taking on the characteristic sickle shape. These sickle cells are prone to clumping together and getting stuck in blood vessels, obstructing blood flow and leading to pain and organ damage.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia
The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can vary from person to person and range in severity. Some people experience mild symptoms, while others have frequent and severe complications. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness: Due to the reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- Pain crises: These are episodes of severe pain, often in the bones, chest, and abdomen, caused by blocked blood vessels.
- Shortness of breath: Resulting from the lungs not receiving enough oxygen.
- Delayed growth and puberty: In children and adolescents.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice): Caused by the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Increased susceptibility to infections: Due to damage to the spleen.
Treatment Options for Sickle Cell Anemia
While there is no cure for sickle cell anemia, several treatments can help manage the symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, and alternative therapies like heat therapy can help alleviate pain during crises.
- Blood transfusions: Receiving regular blood transfusions can increase the number of healthy red blood cells in circulation, reducing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Hydroxyurea: This medication can help reduce the frequency of pain crises and the need for blood transfusions.
- Bone marrow transplant: A bone marrow transplant can potentially cure sickle cell anemia, but it is a risky procedure and not suitable for everyone.
Living with Sickle Cell Anemia
Living with sickle cell anemia requires ongoing medical care and lifestyle modifications. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve quality of life.





