Introduction
Obesity is a growing global health concern, and for many individuals, lifestyle changes alone are not enough to manage their weight effectively. In such cases, bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, can be a life-changing option. Bariatric procedures are designed to help individuals achieve significant weight loss and improve obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and sleep apnea.
This article provides an overview of bariatric procedures, including the different types, their benefits, risks, and what to expect during the recovery process. It's important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if bariatric surgery is the right option for you and to discuss the potential risks and benefits.
Types of Bariatric Procedures
Several types of bariatric procedures are available, each with its own mechanism of action and potential outcomes. Some of the most common bariatric procedures include:
- Gastric Bypass: This procedure involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing a large portion of the stomach.
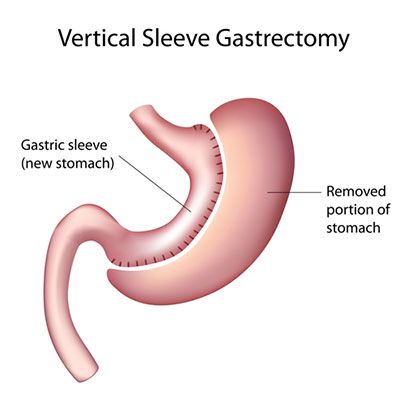
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this procedure, a significant portion of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller, banana-shaped stomach pouch.
- Adjustable Gastric Band: This procedure involves placing an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a smaller pouch that restricts food intake.
Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric procedures can offer significant health benefits for individuals struggling with obesity, including:
- Significant Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery can lead to substantial weight loss, often resulting in a reduction of 50-80% of excess body weight.
- Improvement in Obesity-Related Conditions: Many patients experience significant improvements in obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Weight loss can lead to improved mobility, increased energy levels, and better overall quality of life.
However, like any surgical procedure, bariatric surgery carries potential risks and complications, such as:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: The alterations to the digestive system can lead to nutrient deficiencies, requiring lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation.
- Dumping Syndrome: Some patients may experience dumping syndrome, a condition characterized by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea after eating sugary or high-fat foods.
- Surgical Risks: As with any surgery, there are risks associated with anesthesia and the surgical procedure itself, including infection, bleeding, and complications from anesthesia.
Recovery and Long-Term Lifestyle Changes
After bariatric surgery, patients typically stay in the hospital for a few days and can return to normal activities within a few weeks. However, it's crucial to follow the surgeon's post-operative instructions carefully, including dietary modifications and exercise recommendations.
Bariatric surgery is not a quick fix but rather a tool that, when combined with long-term lifestyle changes, can lead to successful weight management and improved health outcomes. Patients must commit to healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and ongoing medical follow-up to reap the long-term benefits of bariatric surgery.





