Introduction
Hyperlipidemia, commonly known as high cholesterol, is a condition that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by elevated levels of lipids, primarily cholesterol and triglycerides, in the bloodstream. While cholesterol is essential for various bodily functions, excessive levels can lead to serious health problems, particularly cardiovascular disease.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of hyperlipidemia, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and potential health implications. Understanding this condition is crucial for taking proactive steps towards managing cholesterol levels and promoting overall well-being.
Understanding Cholesterol Levels
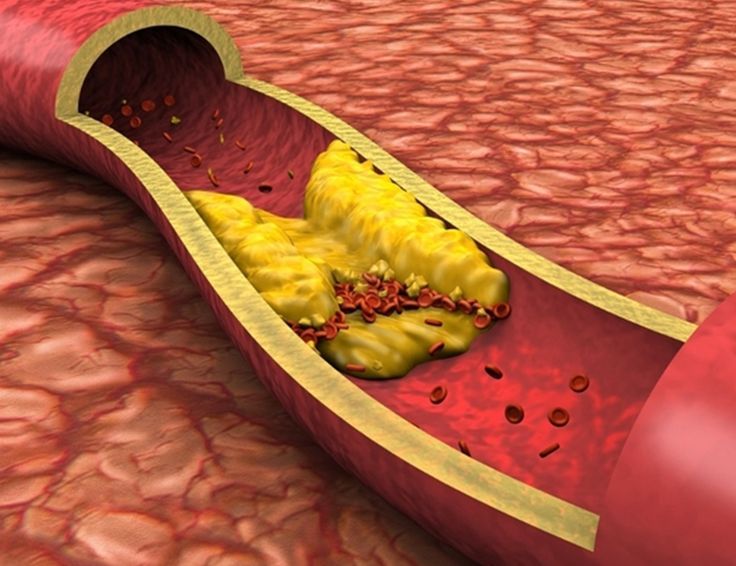
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that plays a vital role in cell membrane formation, hormone production, and vitamin D synthesis. However, an imbalance in cholesterol levels can pose significant health risks. Cholesterol is transported in the blood by lipoproteins, categorized into low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
-
LDL cholesterol ("bad" cholesterol): High levels of LDL cholesterol contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
-
HDL cholesterol ("good" cholesterol): HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, protecting against cardiovascular disease.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia can stem from various factors, including:
-
Genetics: Family history of high cholesterol can significantly increase the risk of developing the condition.
-
Unhealthy lifestyle: Diets high in saturated and trans fats, lack of physical activity, and smoking can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels.
-
Underlying medical conditions: Certain conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease, can lead to hyperlipidemia.
-
Medications: Some medications, like steroids and certain birth control pills, may elevate cholesterol levels.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hyperlipidemia often presents no noticeable symptoms, making regular cholesterol screenings crucial. Diagnosis involves a simple blood test called a lipid panel, which measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Potential Health Implications
Untreated hyperlipidemia can lead to severe health complications, primarily cardiovascular disease. Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup. This process can restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of:
-
Heart attack: Blockage of coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart.
-
Stroke: Interruption of blood flow to the brain.
-
Peripheral artery disease: Narrowing of arteries in the limbs, causing pain and reduced mobility.





