Introduction:
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects people of all ages but often begins in childhood. Eczema can be uncomfortable and distressing, but with proper management, individuals can alleviate symptoms and live full lives. This blog post will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eczema.
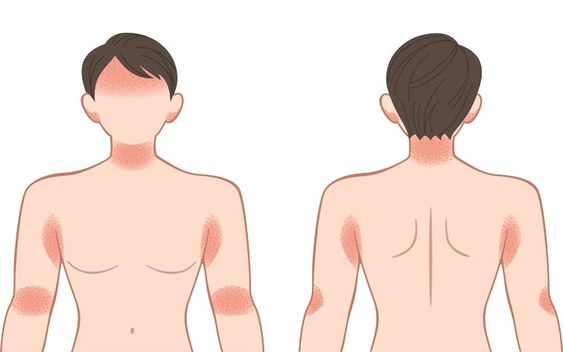
Eczema is a chronic condition, meaning it can last for a long time or come and go in cycles. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more susceptible to developing the condition.
Causes of Eczema:
Several factors contribute to the development of eczema, including:
- Genetics: Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Immune system dysfunction: People with eczema may have an overactive immune system that attacks the skin barrier.
- Environmental triggers: Exposure to irritants, allergens, and dry climates can worsen eczema symptoms. Common triggers include:
- Soaps, detergents, and cleaning products
- Pollen, dust mites, and pet dander
- Certain fabrics, such as wool and synthetic fibers
- Heat, sweating, and low humidity
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate eczema flare-ups.
Symptoms of Eczema:
Eczema symptoms can vary from person to person and range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Dry, itchy skin
- Red, inflamed patches of skin
- Bumps and blisters, which may ooze and crust over
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin
- Skin discoloration
Treatment for Eczema:
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Treatment options often involve a combination of:
- Medications:
- Topical corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors: Suppress the immune response.
- Oral antihistamines: Relieve itching.
- Moisturizers: Hydrate the skin and repair the skin barrier.
- Wet wraps: Provide intensive moisture and soothe inflamed skin.
- Light therapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact eczema management:
- Avoid triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to personal triggers.
- Gentle skincare routine: Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers.
- Lukewarm baths and showers: Avoid hot water, which can dry out the skin.
- Maintain a cool, humidified environment: Use a humidifier during dry months or in arid climates.
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics: Opt for cotton or silk clothing and avoid irritating materials.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.





