Introduction
Addison's disease, also known as adrenal insufficiency, is a rare endocrine disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of certain hormones, primarily cortisol and aldosterone. Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a vital role in helping the body respond to stress, regulate blood sugar, and manage metabolism. Aldosterone helps regulate blood pressure by controlling the balance of salt and water in the body.
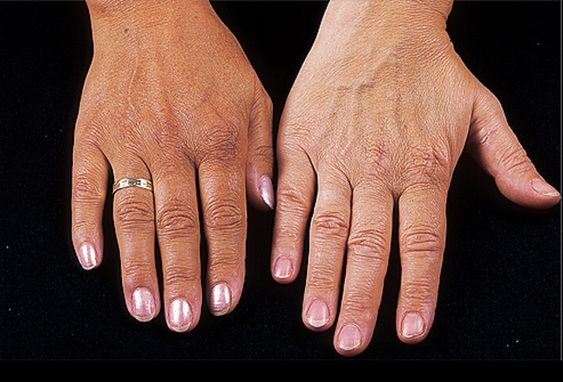
When the adrenal glands are damaged, the production of these essential hormones is impaired, leading to various symptoms. Addison’s disease can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity, but it is relatively uncommon, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 people. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition and preventing potentially life-threatening complications.
Causes of Addison's Disease
Addison's disease can be caused by a range of factors, the most common being an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the adrenal glands. Other potential causes include:
- Tuberculosis: Historically, tuberculosis was a leading cause of Addison's disease.
- Infections: Fungal infections or other infections affecting the adrenal glands.
- Cancer: Tumors in the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland can also lead to adrenal insufficiency.
- Genetic disorders: Rare genetic conditions can affect adrenal gland function.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as those used for long-term steroid therapy, can suppress adrenal function.
Symptoms of Addison's Disease
The symptoms of Addison's disease often develop gradually and can be nonspecific, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Muscle or joint pain
- Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss
- Low blood pressure
- Salt cravings
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation)
Treatment for Addison's Disease
The primary treatment for Addison's disease involves hormone replacement therapy to compensate for the deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. This typically involves taking oral corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone or prednisone, to replace cortisol. In addition, patients may require fludrocortisone to replace aldosterone.
Living with Addison's Disease
With proper management and adherence to treatment, individuals with Addison's disease can lead fulfilling lives. Regular medical checkups are essential to monitor hormone levels and adjust medication dosages as needed. Patients should also be educated about the importance of carrying an emergency medical ID and a dose of injectable corticosteroids in case of adrenal crisis, a life-threatening complication that requires immediate medical attention.





